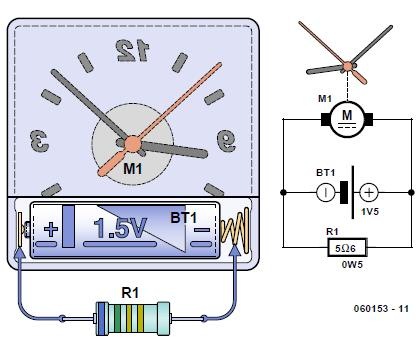
The circuit described here is eminently suitable to indicate the capacity of a battery. We use a cheap electric clock for this. By connecting a resistor across the battery terminals, the battery is discharged somewhat faster than with the clock alone. If we pick a resistor with a value of 5.6 Ω, the discharge current amounts to 1.2 V / 5.6 Ω = 214 mA. If we multiply this with the number of hours that the clock ran after the battery was connected up then we know (approximately) the capacity of the battery.
When discharging a NiCd battery we need to make sure we remove the battery the moment the clock stops running. NiCd batteries do not tolerate too deep a discharge very well. We therefore recommend keeping an eye on the voltage in one way or another, for example by connecting a multimeter in parallel with the resistor.
Author: J. Van der Sterre
(Elektor Electronics Magazine 2006)
 | * Download this article. |
Labels
- * Elektor 2005 (9)
- * Elektor 2006 (72)
- Adapters (1)
- ADC / DAC (1)
- AM / FM (2)
- Amplifiers (3)
- Antennae (2)
- Articles List (1)
- Audio (1)
- Automatic (2)
- Batteries (3)
- Bluetooth (1)
- Breakers / Contacts (1)
- Buzzers / Sirens (1)
- Clocks / Timers (2)
- Computer (2)
- Converters (2)
- Coolers / Fans (1)
- Counters (1)
- Datasheets (7)
- E-blocks (1)
- Energy (2)
- Flash / Light (8)
- Frequency (1)
- Fuse (1)
- Generators (2)
- High-voltage (1)
- Indicators (2)
- Infrared (IR) (4)
- LCDs (1)
- LEDs (7)
- Magazines (1)
- Meters (5)
- Microcontroller (9)
- Mobile Phone (1)
- Motors (1)
- OPAMP (3)
- PCB (1)
- Photosensors (1)
- Power Supply (2)
- Preamplifiers (1)
- Programming (3)
- Radio (1)
- Rectifiers (1)
- Regulators (1)
- Relays / Switches (10)
- Remote Control (7)
- RS232 (3)
- Security (4)
- Sensors (2)
- Servo (2)
- Simulators (1)
- Small Circuits (46)
- Telephones (2)
- TENS (1)
- Testers (3)
- Timebase (1)
- Tools (1)
- Transmitters (1)
- Trigger (1)
- USB (2)


0 comments: