
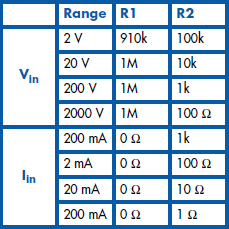
In order to measure higher voltages we have to reduce the voltage with a potential divider. For this purpose we add R1 and R2. R1 is connected in series with the + input of the module and R2 is connected in parallel with the inputs. In the table we can see the correct ratios of R1 and R2. These modules typically have an input impedance of more than 10 MΩ. With the attenuator in front of it the input impedance reduces to 1 MΩ, still high enough for most measurements.
To measure current with a voltmeter we first hav e to convert the current into an equivalent voltage. Resistor values for doing this are also shown in the table.

In contrast with the input impedance of a voltmeter, the input impedance of a current meter needs to be as low as possible. The input impedance of this circuit depends on the range and is practically identical to the value of R2. As a consequence, keep in mind that there is a voltage drop across the meter of up to 0.2 V. When making measurements you have to take into account that lethal voltages can be present in the circuit, particularly with the 200-V and 2000-V ranges. In addition, the specifications of your ordinary, common or garden resistor do not permit these kinds of voltages. When measuring these high voltages suitable resistors need to be used.
(Elektor Electronics Magazine – 07/2006)
 | Download this article (#040037uk.pdf) |
Labels
- * Elektor 2005 (9)
- * Elektor 2006 (72)
- Adapters (1)
- ADC / DAC (1)
- AM / FM (2)
- Amplifiers (3)
- Antennae (2)
- Articles List (1)
- Audio (1)
- Automatic (2)
- Batteries (3)
- Bluetooth (1)
- Breakers / Contacts (1)
- Buzzers / Sirens (1)
- Clocks / Timers (2)
- Computer (2)
- Converters (2)
- Coolers / Fans (1)
- Counters (1)
- Datasheets (7)
- E-blocks (1)
- Energy (2)
- Flash / Light (8)
- Frequency (1)
- Fuse (1)
- Generators (2)
- High-voltage (1)
- Indicators (2)
- Infrared (IR) (4)
- LCDs (1)
- LEDs (7)
- Magazines (1)
- Meters (5)
- Microcontroller (9)
- Mobile Phone (1)
- Motors (1)
- OPAMP (3)
- PCB (1)
- Photosensors (1)
- Power Supply (2)
- Preamplifiers (1)
- Programming (3)
- Radio (1)
- Rectifiers (1)
- Regulators (1)
- Relays / Switches (10)
- Remote Control (7)
- RS232 (3)
- Security (4)
- Sensors (2)
- Servo (2)
- Simulators (1)
- Small Circuits (46)
- Telephones (2)
- TENS (1)
- Testers (3)
- Timebase (1)
- Tools (1)
- Transmitters (1)
- Trigger (1)
- USB (2)


0 comments: